In a world where access to clean drinking water remains a cornerstone of healthy living, the quest for efficient and reliable water purification technologies has never been more critical. Among the myriad of solutions available, Reverse Osmosis Water Filter Systems stand out as a beacon of hope for households and businesses alike. This sophisticated technology harnesses the power of reverse osmosis, a process that eliminates contaminants from water by passing it through a semipermeable membrane, thereby ensuring that every drop is not only safe but also tastes great. As concerns over water quality and safety continue to grow, reverse osmosis presents a scientifically proven, cost-effective method to access pure water directly from the tap, reaffirming the essential role of clean water in sustaining life and well-being in modern society.
What is Reverse Osmomis Water Filter System?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a sophisticated water purification technology that has become synonymous with providing clean and safe drinking water. At its core, reverse osmosis is a process whereby water molecules are forced through a semipermeable membrane, a barrier that allows only water to pass while rejecting larger molecules and a wide array of contaminants, from dissolved salts to bacteria and viruses.
The principle behind reverse osmosis is based on applying pressure to overcome natural osmotic pressure, a colligative property driven by chemical potential, a measure of the substance’s potential to undergo change. In simpler terms, in natural osmosis, water flows from a lower concentration of solutes to a higher concentration through a semipermeable membrane to equalize concentrations on both sides. However, in reverse osmosis, pressure is applied to the higher concentration side, reversing the natural flow, thus allowing pure water to be collected from the side of the membrane where contaminants are left behind.
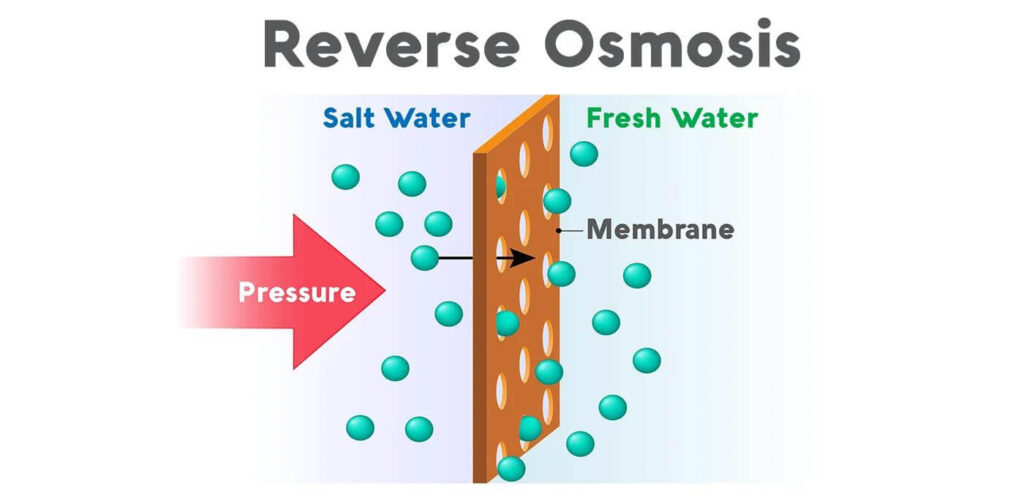
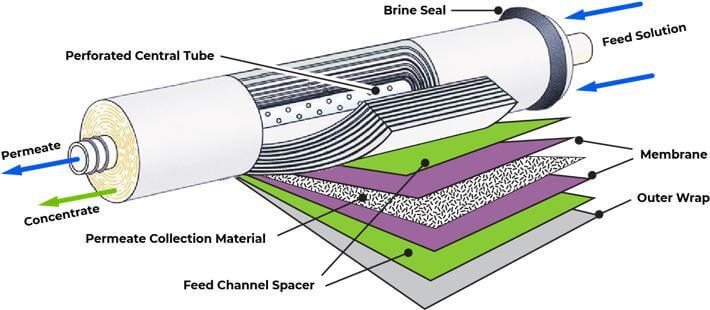
Components of a Reverse Osmosis System
A Reverse Osmosis (RO) system includes several key components, each marked with its distinct role in ensuring the purification process’s efficiency:
- RO Membrane: This semi-permeable barrier is crucial, allowing only water molecules to pass while blocking a vast array of contaminants. It’s the core component responsible for the significant reduction of dissolved solids and impurities.
- Sediment Filter: Positioned at the initial stage of filtration, it captures and holds particles such as dirt, dust, and rust, preventing these elements from reaching and clogging the RO membrane.
- Carbon Filter: This filter removes chlorine and organic compounds, enhancing the taste and smell of water and protecting the RO membrane from chemical damage.
- Post-filter: After the water has passed through the RO membrane, it goes through this additional filter to polish the water, removing any residual taste or odors and ensuring the water’s quality.
- Storage Tank: The purified water is stored in this tank until it’s dispensed, providing a continuous supply of clean water on demand.
- High-Pressure Pump: Essential for the RO process, this pump applies the necessary pressure to push water through the RO membrane, overcoming the natural osmotic pressure.
- UV Light: Some systems include this feature for an extra layer of purification, using ultraviolet light to kill or inactivate microorganisms, ensuring the water is free from biological contaminants.
- Faucet: Mounted on the sink, it serves as the delivery point for the purified water, making it accessible for use.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the RO system, working together to ensure that the water is purified efficiently and effectively, making it safe for consumption.

The Process: How Does a Reverse Osmosis Filter System Work?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water filter systems are sophisticated solutions for purifying drinking water, utilizing a multi-step process to eliminate a broad spectrum of impurities. Here’s a breakdown of how these systems function to ensure the delivery of clean, safe water:
Step 1: Pre-filtration
The process begins with water passing through pre-filters, typically including a sediment filter and a carbon filter. The sediment filter captures large particles such as sand, dirt, and rust. Following this, the carbon filter removes chlorine, odors, and any volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This initial stage is vital for protecting the RO membrane from damage by larger particles and chemical substances, thereby extending its lifespan and efficiency.
Step 2: The Heart of the Process:Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The core of the system is the RO membrane, a semi-permeable layer that allows only water molecules to pass through while blocking nearly all dissolved solids, metals, and harmful contaminants. Water is pushed against this membrane under high pressure, a critical step that ensures the removal of up to 99% of impurities. The purity of the water achieved at this stage is unparalleled, making it the most crucial phase of the RO process.
Step 3: Specialty Filtration
To further refine water quality, some RO systems incorporate additional filtration stages designed to target specific contaminants that may have bypassed previous stages. These can include filters specialized for removing lead, mercury, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and even microbial threats such as viruses, cysts, and bacteria.
Step 4: Drainage and Storage
Following the rigorous filtration process, the system expels any remaining wastewater, a byproduct of purification. The efficiency of an RO system in managing wastewater can vary, with some models designed to be more efficient than others. The purified water is then stored in a tank until needed, ensuring a constant supply of clean water for drinking and cooking.
Step 5:Additional Polishing Step
For an even higher quality of water, some RO systems include a final polishing step. This occurs when the tap is turned on, activating an additional filter that further enhances the taste and purity of the water, delivering a final product that is as refreshing as it is clean.
The significance of each stage in the RO process cannot be overstated. Together, they ensure the removal of a wide array of contaminants, including particles, chemicals, and microorganisms, making the water safe for drinking and cooking. By systematically addressing various impurities at each phase, RO systems provide a comprehensive solution for water purification, delivering clean and safe drinking water that meets the highest standards of quality.
What Contaminants Does Reverse Osmosis Remove from Water?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water filtration systems are adept at removing a comprehensive list of contaminants from water, offering a safeguard against various health hazards. The RO membrane’s fine pore structure is key to its effectiveness, capable of filtering out:
| Contaminant Type | Examples | Health Risks Reduced |
|---|---|---|
| Dissolved Salts and Minerals | Sodium, chloride, fluoride, potassium | Prevents issues related to high mineral intake |
| Heavy Metals | Lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic | Reduces risk of neurological damage, cancer |
| Chemical Contaminants | Pesticides, herbicides, VOCs | Lowers exposure to harmful chemicals linked to various health issues |
| Microorganisms | Bacteria, viruses, protozoa | Prevents waterborne diseases |
| Pharmaceutical Residues | Prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications | Minimizes unknown health effects from drug contamination |
| Nitrates and Sulfates | Found in agricultural runoff | Protects against methemoglobinemia in infants, digestive disturbances |
By targeting this broad spectrum of contaminants, RO systems significantly reduce the risk associated with consuming impure water. The removal of such substances is crucial for maintaining health, as many of them are linked to various short-term and long-term health effects, including gastrointestinal illness, reproductive problems, and neurological disorders. The thorough purification process of RO ensures that water is not just safe to drink but also of superior taste and quality, providing an essential layer of protection in maintaining overall well-being.
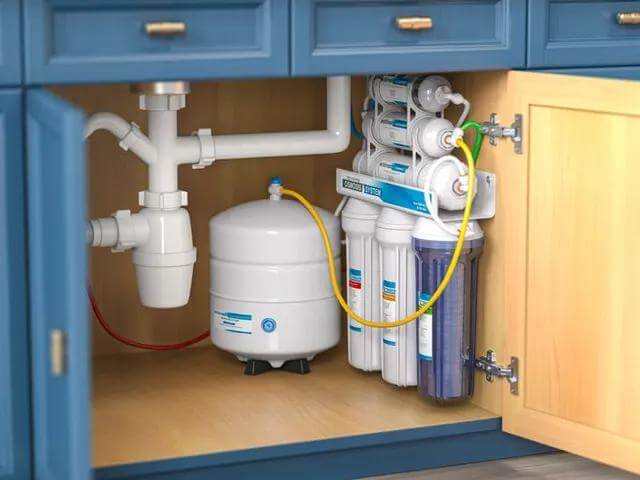

Reverse Osmosis Water Filter System Pretreatment and Maintenance
Pretreatment is a crucial step in the reverse osmosis (RO) water filtration system, designed to protect the RO membrane and ensure the system’s longevity and efficiency. Pretreatment involves removing larger particles and chlorine from the water before it reaches the RO membrane. This is typically achieved through sediment and carbon filters. Sediment filters catch dust, dirt, and rust, which could clog the membrane, while carbon filters remove chlorine and volatile organic compounds that can damage the membrane’s delicate surface. This preliminary process helps in maintaining the integrity of the membrane and ensures that the system can effectively remove the finer contaminants during the RO process.
Regular maintenance is vital to keep an RO system functioning optimally. This includes changing pre- and post-filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, usually every 6 to 12 months. The RO membrane itself typically needs replacement every 2 to 3 years, depending on the water quality and the amount of water processed. It’s also essential to periodically check the system for leaks and to sanitize the storage tank annually to prevent bacterial growth. Properly maintaining an RO system not only extends its life but also ensures that the water quality remains high, providing safe and clean drinking water. Ignoring maintenance schedules can lead to decreased water quality, reduced water flow, and ultimately, system failure.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and ensuring the appropriate pretreatment steps are taken, users can maximize the efficiency of their RO system, guaranteeing a consistent supply of pure, great-tasting water for years to come.
Enhancements and Adjustments
Enhancements and adjustments, such as incorporating a booster pump and adjusting water pressure and pH levels, can significantly optimize the performance of reverse osmosis (RO) systems.
Role of a Booster Pump
A booster pump plays a pivotal role in RO systems, especially in situations where the incoming water pressure is lower than the ideal level required for optimal RO operation. The effectiveness of an RO system is heavily reliant on sufficient pressure to push water through the RO membrane to filter out contaminants effectively. A booster pump increases the water pressure to optimal levels, ensuring the system functions efficiently, improves the purity of the water, and increases the production rate of filtered water. Additionally, it can help reduce the amount of wastewater generated by the system.
Adjusting Water Pressure and pH Levels
Water pressure adjustment is crucial for the RO system’s performance. Inadequate water pressure can lead to poor water production and reduced contaminant removal efficiency. By adjusting the water pressure to the ideal range, usually between 40-60 psi, the system can operate more effectively, producing high-quality water at a faster rate.
The pH level of RO water is another aspect that may require adjustment. RO filtering can remove minerals, resulting in slightly acidic water with a lower pH. While this is generally safe, some users prefer to neutralize the pH to be closer to neutral (pH 7). This can be achieved by adding a remineralization stage after the RO process, which not only increases the pH but also adds back beneficial minerals that were removed, enhancing the water’s taste and making it more alkaline.
Incorporating enhancements like a booster pump and adjusting key factors such as water pressure and pH levels are essential steps in maintaining the efficiency and effectiveness of RO systems. These adjustments ensure that users have access to not only safe but also palatable drinking water, tailored to their preferences and health requirements.

What is different between RO Systems and Water Filters?
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems and standard water filters serve the common purpose of purifying water but differ significantly in their methods and efficiency of filtration.
Differences Between RO Systems and Standard Water Filters
Mechanism of Filtration: Standard water filters typically use a physical barrier, such as activated carbon or sediment filters, to remove contaminants from water. These filters are effective at reducing chlorine, bad tastes, odors, and some sediments. On the other hand, RO systems employ a multi-stage process that includes sediment and carbon filtration but crucially incorporates a semi-permeable membrane that can remove up to 99% of dissolved salts, tiny particles, and organic molecules, making it significantly more thorough.
Range of Contaminants Removed: While standard filters are effective for improving taste and removing some chemicals and particulates, RO systems are capable of eliminating a broader spectrum of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, fluoride, and other dissolved substances not addressed by most standard filters.
Water Quality: The result of the RO process is water that is not only free from contaminants but also balanced in terms of pH, making it ideal for drinking and cooking. Standard filters can improve water quality but do not offer the same level of purification and may leave behind various dissolved impurities.
Advantages of Choosing an RO Water Filter
Comprehensive Purification: RO systems provide a comprehensive solution for water purification, offering peace of mind for users concerned about a wide range of contaminants. This makes RO filtered water among the cleanest and safest for consumption.
Taste and Odor: The multi-stage filtration process, including the post-filtration polishing filters found in RO systems, significantly improves the taste and odor of water, often surpassing the capabilities of standard water filters.
Cost-Effectiveness: Though RO systems may have a higher initial cost, their ability to purify water to a higher standard can make them more cost-effective in the long run, especially in areas with heavily contaminated water or for those relying on bottled water.
Health Benefits: By removing harmful contaminants, RO systems can reduce the risk of health issues associated with polluted or hard water, providing long-term benefits to the user’s health.

In conclusion, while standard water filters are suitable for basic filtration needs, RO systems offer a more advanced and comprehensive solution for those seeking the highest quality of water purification. The choice between the two should be based on the specific needs, water quality in your area, and the level of purification desired.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
1. Exceptional Purity: RO systems are capable of removing up to 99% of dissolved salts, particles, bacteria, viruses, and chemicals, providing water that is of significantly higher purity compared to standard filtration.
2. Improved Taste and Odor: The removal of contaminants and minerals results in water that tastes better and is free of odors, enhancing the overall drinking experience.
3. Cost Efficiency: Over time, using an RO system can be more cost-effective than buying bottled water, offering a sustainable solution for high-quality drinking water at home.
4. Health Benefits: By eliminating harmful contaminants, RO filtered water can reduce the risk of certain health issues related to waterborne pollutants, leading to improved overall health.
5. Low Maintenance: Despite their complex filtration process, RO systems require relatively low maintenance, needing only periodic filter changes.
Drawbacks and Considerations
1. Initial Cost and Installation: The upfront cost for an RO system can be higher than other types of filters, and installation may require professional assistance, adding to the initial expenses.
2. Water Wastage: RO systems produce wastewater in the purification process. The ratio of pure water to wastewater varies by system, and in some cases, this can be a significant amount, which may be a consideration in areas with water scarcity.
3. Removal of Beneficial Minerals: RO filtration can also remove certain beneficial minerals from water. Some systems address this by reintroducing essential minerals back into the water post-filtration.
4. Slow Filtration Rate: The process of reverse osmosis takes time, which means RO systems can have a slower output compared to basic filters. This is usually mitigated by the use of a storage tank.
5. Space Requirements: Depending on the model, an RO system can require significant under-sink space or wherever it is installed, which might be a constraint in smaller kitchens.
When considering the installation of a reverse osmosis water filter system, weighing these benefits against the drawbacks is crucial. The decision should factor in your specific needs, water quality concerns, and environmental considerations. While the benefits of purified, safe, and tasty drinking water are clear, the efficiency and sustainability of the system are also important to consider.
Conslusion
Clean drinking water is vital for health, and Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems play a key role in providing this. By removing a wide range of contaminants, RO technology ensures water is not just safe, but of the highest quality. Considering RO systems for your water purification needs means investing in health, peace of mind, and superior water quality. It’s a step towards ensuring you and your family have access to the best possible drinking water.

FAQ
1. What is reverse osmosis (RO) in water filtration?
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that removes impurities from water by pushing it under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. The membrane allows water molecules to pass through while blocking larger molecules and contaminants, such as salts, bacteria, viruses, and chemicals.
2. How does a reverse osmosis water filter system work?
A reverse osmosis water filter system works in stages, including pre-filtration (to remove sediment and chlorine), reverse osmosis (where water is pushed through the RO membrane), and post-filtration (to polish the water and remove any remaining taste and odor). The result is clean, purified water.
3. What contaminants can reverse osmosis remove?
Reverse osmosis can remove a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts (ions), particles, colloids, organics, bacteria, and pyrogens. However, it’s important to note that some chemicals like chlorine and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) require additional filtration steps.
4. Is reverse osmosis water safe to drink?
Yes, reverse osmosis water is safe to drink. The process effectively removes contaminants and impurities, producing water that is clean and safe for consumption. However, it’s essential to maintain the system properly to ensure the quality of the water.
5. Does reverse osmosis remove beneficial minerals from water?
Yes, reverse osmosis can remove some beneficial minerals along with contaminants. However, many RO systems include a remineralization stage to add essential minerals back into the water, balancing its pH and improving taste.
6. How often do reverse osmosis filters need to be replaced?
The frequency of filter replacement depends on the quality of the input water and the amount of water used. Typically, pre-filters and post-filters should be replaced every 6-12 months, while the RO membrane can last 2-3 years. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
7. Can reverse osmosis systems waste water?
Yes, reverse osmosis systems can produce waste water, known as brine or concentrate, which contains the removed contaminants. The efficiency and design of the RO system affect the amount of waste water produced. Modern systems are designed to minimize waste.
8. How do I maintain my reverse osmosis water filter system?
Regular maintenance includes replacing filters and membranes according to the manufacturer’s schedule, checking the system for leaks, and cleaning the storage tank. Proper maintenance ensures the system operates efficiently and produces high-quality water.
9. What is the difference between reverse osmosis and other filtration methods?
Reverse osmosis differs from other filtration methods in its ability to remove a broader range of contaminants, including very small particles and dissolved substances. Other methods, such as activated carbon filtration, target specific chemicals and improve taste and odor but may not remove dissolved salts or minerals.
10. How does water pressure affect a reverse osmosis system?
Water pressure is crucial for the efficiency of a reverse osmosis system, as it drives the water through the RO membrane. Low water pressure can result in reduced water flow and decreased contaminant removal efficiency. Most RO systems require a minimum pressure of 35-40 psi to operate effectively, and some come with a booster pump to maintain optimal pressure.
